As LLMs, agents, and generative systems are embedded into everything from customer service to legal ops, we’re entering a new security era.
AI systems are being deployed faster than they’re being secured. Traditional cybersecurity frameworks weren’t built to handle things like prompt injection, agent drift, or probabilistic model behavior.
“Why LLMs, Agents, and AI Systems Need Dedicated Security Frameworks.”
Why AI is the next major attack surface
Real-world breaches you might’ve missed (Samsung, OpenAI, Bing/Sydney)
How to embed AI-specific controls into your existing stack
Regulatory moves that will impact how we build and audit AI systems
AI security isn’t just a niche, it’s the next evolution of cybersecurity.
We can’t defend neural networks with frameworks built for networks.
Why LLMs, Agents, and AI Systems Need Dedicated Security Frameworks
AI is no longer just a feature, it's becoming infrastructure. Large language models (LLMs), autonomous agents, and generative AI tools are being embedded in customer service, analytics, coding, legal work, and more.
But while adoption accelerates, security practices haven’t caught up.
This whitepaper explains why AI security is the next evolution of cybersecurity, what threats enterprises face, and how to integrate AI-specific controls into your existing security architecture.
In the early 2000s, businesses scrambled to secure websites and cloud apps. Today, we’re facing a similar inflection point with AI as a new digital layer.

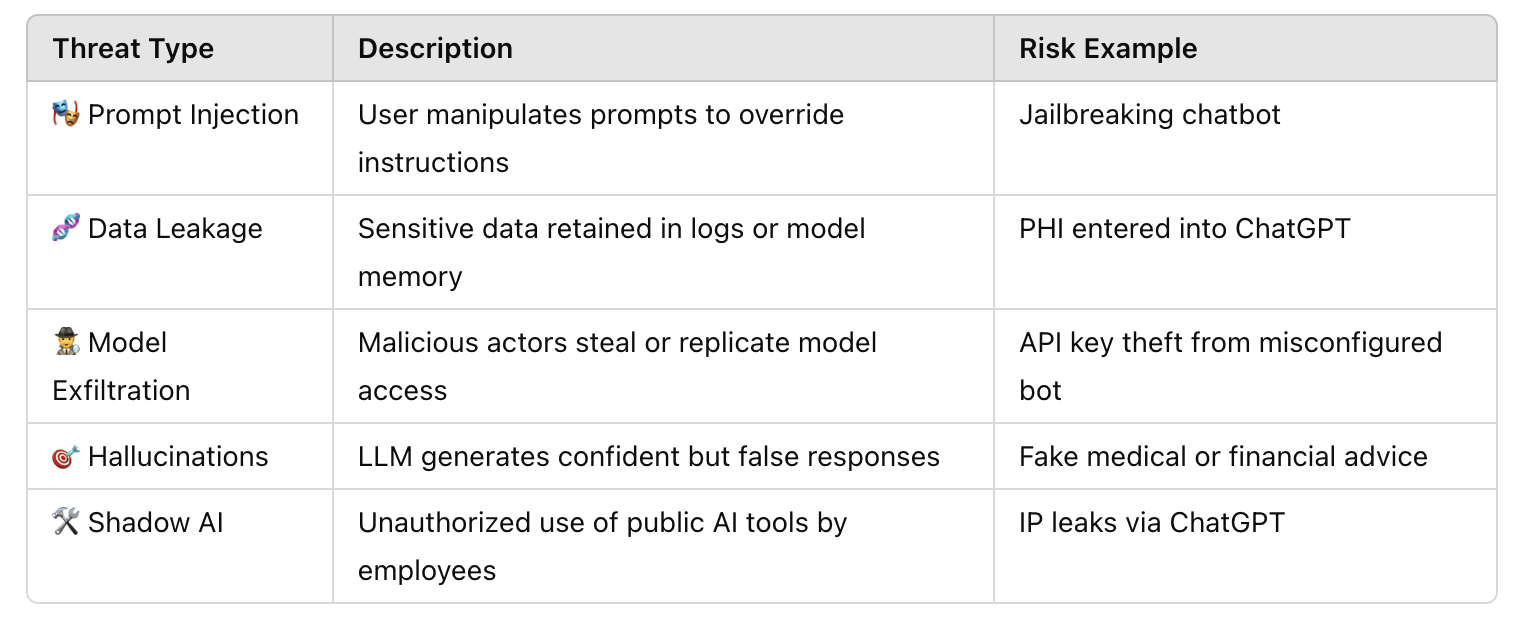
According to ENISA's 2023 AI Threat Landscape, AI systems face distinct attack vectors, not covered by traditional security controls.
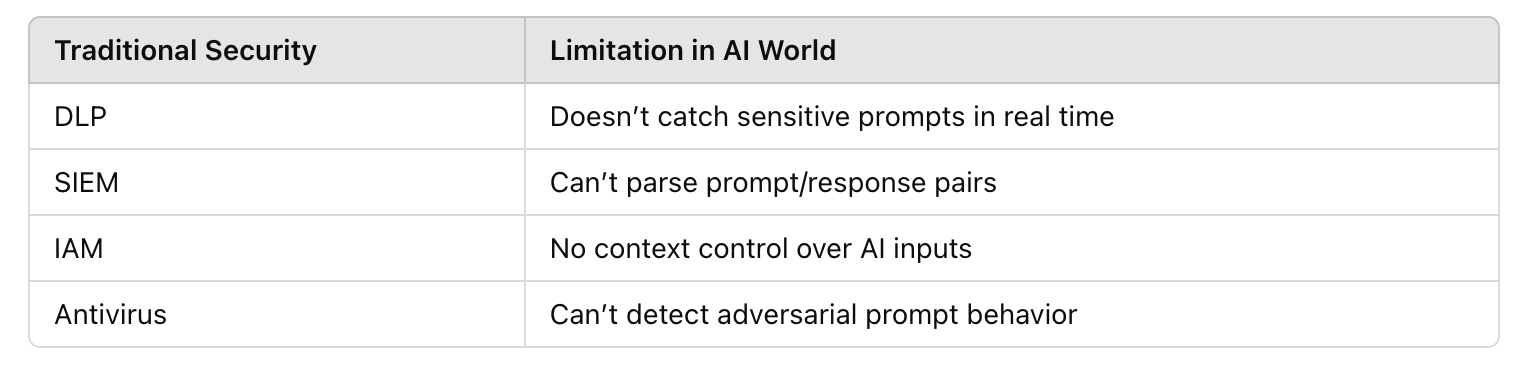
LLMs introduce probabilistic behavior, making them harder to secure with deterministic tools.
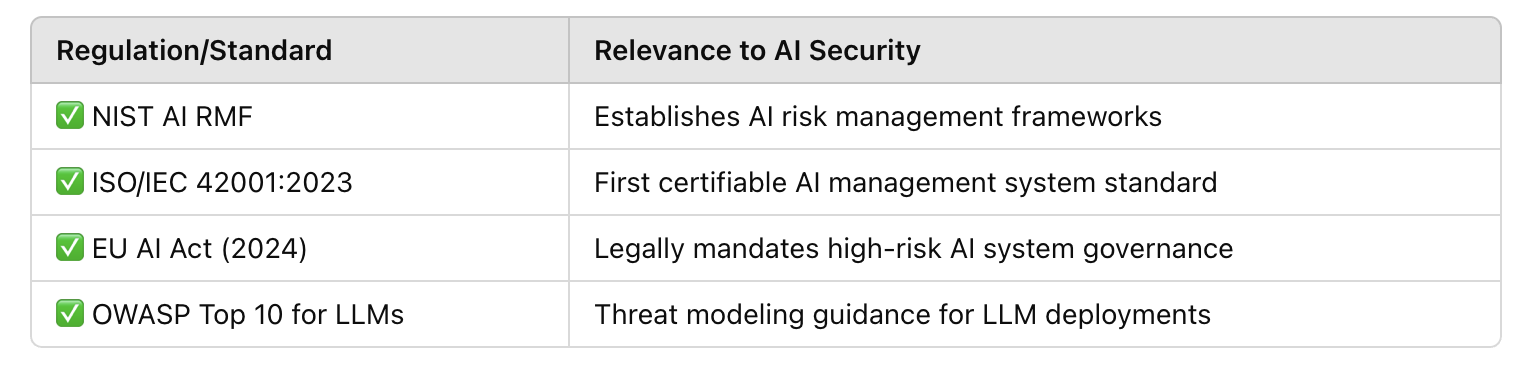
By 2026, Gartner predicts 70% of enterprises will be required to audit AI use for compliance
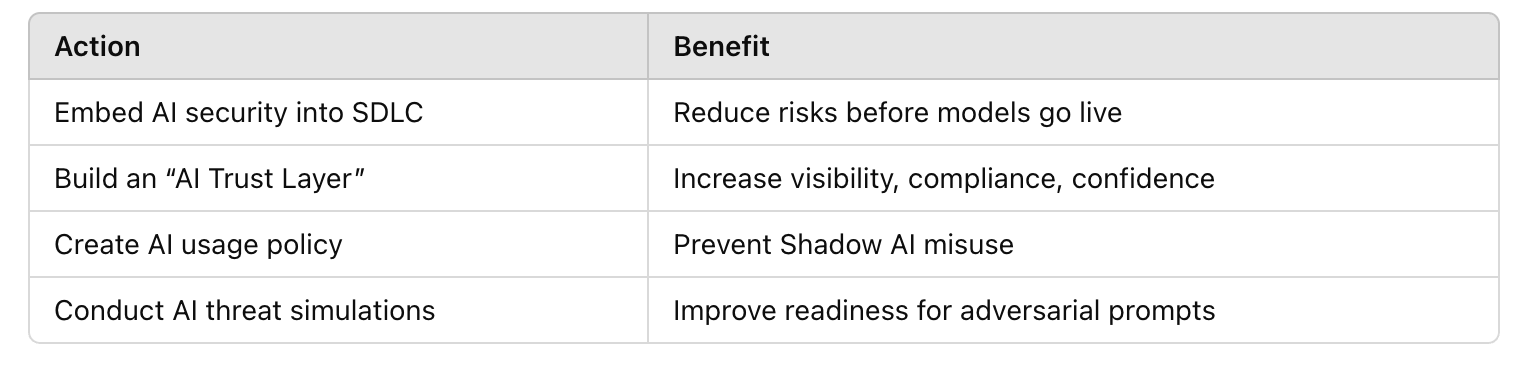
From prompt manipulation to compliance exposure, enterprises must evolve their security mindset and their stack. Treating AI security as an extension of cybersecurity is no longer enough. It’s time to give it first-class status.